When periodontal disease is detected early in its onset, conservative or non-surgical methods of care in combination with improved hygiene routines can restore periodontal health. While periodic, professional cleanings are sufficient to maintain periodontal health in patients that do not have gum disease, once gingivitis is present, deeper cleanings and possibly other non-surgical methods of care are recommended to treat the condition.
The American Academy of Periodontology emphasizes achieving periodontal health by means of the least invasive and cost effective treatment approaches to care. Deeper cleanings, which include Scaling and Root planing, are non-surgical procedures that are considered the first line of defense against the progression of periodontal disease.
With scaling and root planing, any plaque and tartar (hardened dental plaque) that have accumulated below the gumline are carefully removed and then the root surfaces of the teeth are smoothed. Since, periodontal disease is an inflammatory response to plaque, tartar and bacterial toxins, by simply mechanically eliminating these agents, the progression of gum disease can be halted. In addition to removing plaque and tartar with a scaling and root planing procedure, antimicrobial medication placed under the gumline or systemic medications can be used as adjuncts to care to further reduce the bacterial population.
If non-surgical approaches to managing periodontal disease do not achieve the desired outcome, surgery may be recommended to halt its progression and repair damage as possible.
When gum disease has advanced beyond the initial stage, periodontal surgery is often recommended to effectively remove bacteria and tartar from around the teeth, reduce gingival pocket depth, restore lost tissue as possible and halt the disease process. Untreated gum disease is a progressive condition, which will continue to compromise the appearance of one's smile, dental health, oral function and overall well being if the appropriate measures are not taken.
With proper surgical treatment and maintenance care, the chances of tooth loss, further damage to the bone and soft tissues supporting the teeth, and complications from health problems that are linked to periodontal disease can be decreased.
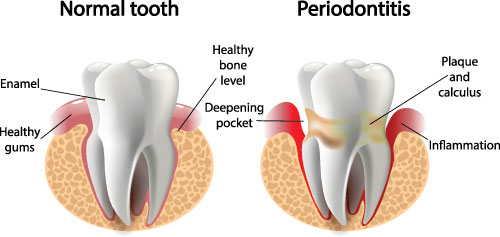
Gum disease is typically the result of inadequate or ineffective oral hygiene practices that lead to the accumulation of dental plaque, which is sticky film that is colonized by oral bacteria. The harmful bacteria and the products they produce provoke a defensive, inflammatory response in the gums. When this inflammation is not resolved, tissue damage ensues and spaces between the gums and teeth that are known as periodontal pockets develop. As the periodontal pockets deepen, the bacteria become more difficult to remove and the gaps between the surface of the teeth and gums get larger. When pocket depth increases to the point of being beyond the reach of deep cleanings and other conservative methods of care (5mm or more), gum surgery to clean and treat the damage to gums and underlying bone is recommended.
By performing pocket reduction surgery the following is accomplished:
While a surgical procedure known as flap surgery during which the tissue is surgically reflected away from the teeth and bone so that the area can be treated before the tissue is sutured back into place, is typically performed, some practitioners are now using soft tissue laser procedures to reduce pocket depth.
Crown lengthening is a common procedure that is routinely performed to re-contour gum tissue and bone, as needed, with the intent of making more tooth structure available for the placement of a dental crown or dental bridge. This is often the case when a tooth is decayed or otherwise damaged below the gum line.
Alternatively, a crown lengthening procedure can also be performed for reasons that are purely aesthetic to reduce the appearance of a "gummy smile" when too much of the gums and far too little tooth structure is displayed when smiling. It can be performed on a single tooth to make the gum line appear even with the other teeth or on several teeth to improve a smile's overall appearance.
In addition to the development of pockets and bone loss, periodontal disease can cause the gums to recede, thereby exposing the roots of the teeth. When the root of a tooth loses its overlying soft tissue, it becomes more vulnerable to decay, sensitivity and additional bone loss. Gum recession also takes a toll on smile aesthetics. Having front teeth affected by this problem can make a broad smile less aesthetically appealing as uncovered root structure is displayed. While gum recession is often a consequence of gum disease, aggressive tooth brushing and other habits can also wear away gum tissue.
By performing a gum graft procedure, which is also known as a "gingival graft or soft tissue graft," the dentist replaces the soft tissue over the exposed area of the tooth to address the problems created by receding gums. Gum tissue for grafting procedures can be harvested from a nearby site in the mouth or obtained from another donor source. A gum graft may be performed on a single tooth or multiple ones. And, based upon the needs of the case, the dentist will determine which type of gum graft to employ.
The three types of gum grafts include the following:
Following a gum graft procedure, the dentist will provide detailed post-operative care instructions as well as set up appointments to make sure the surgical site is healing properly and to check that the graft is successful.
Bone loss in the jaws and around the teeth can be the result of missing teeth, periodontal disease, or trauma. This bone loss is more than a detriment to oral health and function; it can also alter facial appearance as the support for the natural contours of the face is diminished.
When a tooth is extracted, the natural stimulation to the underlying bone that is generated by the forces of biting or chewing is lost. In fact, bone width can be reduced by as much as 25% in the first year following tooth loss.
With grafting procedures, the dental bone can be restored to its original dimensions to maintain facial esthetics, repair the damage caused by periodontal disease as well as facilitate the success of procedures such as the placement of dental implants. A bone graft provides a platform or "scaffolding" for new bone growth and the material for a bone graft can be derived from the patient, other donor sources or be comprised of synthetic, bone-like materials.
There are several types of grafting procedures that can be performed with the particular approach depending upon the needs of the case.
A bone graft can be placed immediately upon the extraction of a tooth or some time after tooth loss. Placing a bone graft at the time of tooth removal reduces the amount of bone loss in the area to maintain the hard tissue support that is required for the future placement of a dental implant. When a bone graft is placed awhile after tooth loss, a separate surgical procedure is required to reflect the soft tissue, expose the underlying bone, place a graft and then suture the soft tissue back into place.
For patients lacking a sufficient amount of bone for a dental implant to replace a maxillary back tooth (upper back tooth), a procedure known as a "sinus lift" may be performed. During this surgical procedure, the sinus membrane is lifted and bone graft material is added between the jaw and the floor of the sinus to provide the needed bone height to successfully support a dental implant.
In addition to bone grafting for purposes of ridge preservation or augmentation to allow for dental implants, an aesthetic ridge augmentation procedure to restore the natural contours of the bone is sometimes performed in preparation for fixed bridgework to achieve a more cosmetically pleasing result.
To guide tissue regeneration as well as protect the graft and promote healing, special membranes and biologically active materials may be placed over the grafting material.
Dr. Dan has been voted as one of America's Top Dentists by the Consumer Research Council of America in 2018. This accomplishment is based on his experience, training, and membership in professional organizations. In addition to his dental training, Dr. Dan has received advanced specialized training in dental implant surgery, in which he is a Fellow of the International Congress of Oral Implantologists and in Orthodontics focused on Invisalign.
Requirements of Fellow of the International Congress of Oral Implantologists: